How Commercial Insulation Affects Workplace Comfort and Productivity
Commercial insulation directly impacts workplace comfort and productivity by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures,
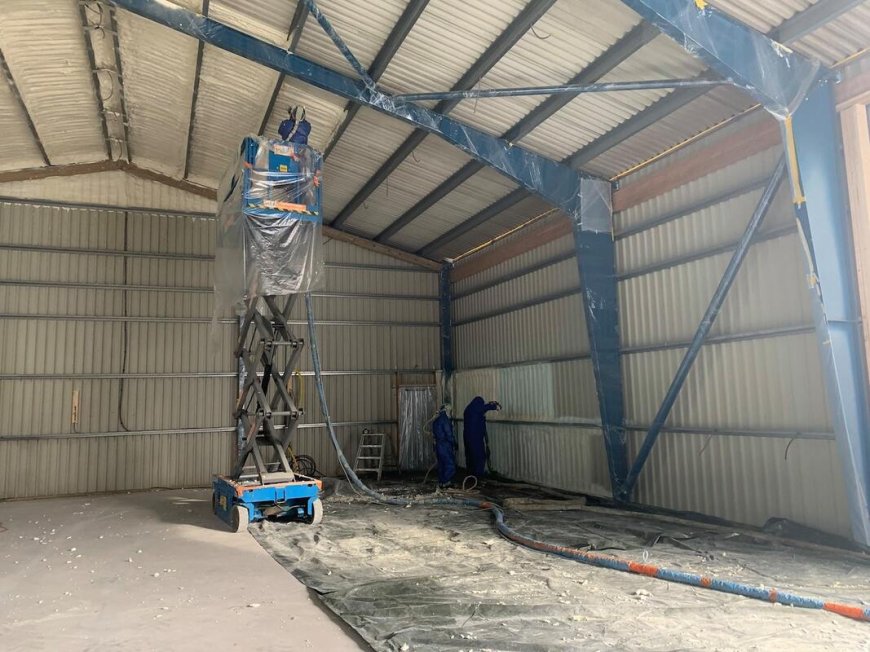

Commercial insulation directly impacts workplace comfort and productivity by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures, reducing noise transmission, and controlling humidity levels. Properly installed insulation systems improve employee performance by 6-9% while reducing absenteeism by up to 15% through enhanced thermal comfort and acoustic control. The building envelope's thermal performance determines energy stability, indoor air quality, and occupant satisfaction across all commercial spaces.
Effective insulation strategies create stable work environments that optimize human performance while reducing operational demands on HVAC systems. This comprehensive analysis examines how insulation materials and installation methods influence employee comfort, productivity metrics, and overall workplace functionality.
Temperature Stability and Employee Performance
Consistent indoor temperatures maintain optimal cognitive function and physical comfort throughout the workday. Research demonstrates that temperatures outside the 68-76F range reduce productivity by 2% for each degree of deviation. Thermal fluctuations create discomfort that forces employees to adjust clothing, seek alternative work locations, or experience concentration difficulties.
Commercial insulation systems prevent heat transfer through building envelopes, maintaining stable interior conditions regardless of outdoor weather variations. Well-insulated buildings require less HVAC cycling, reducing temperature swings that disrupt workplace comfort. The thermal mass effect of proper insulation dampens rapid temperature changes during peak heating and cooling periods.
Bonus Tip: Open office layouts benefit most from continuous insulation strategies because thermal variations affect larger groups of employees simultaneously.
Cognitive Function and Thermal Comfort
Temperature extremes directly impair mental performance through physiological stress responses. Cold environments reduce fine motor skills and typing accuracy, while excessive heat causes fatigue and decreased attention spans. The human body expends energy maintaining core temperature when ambient conditions exceed comfort ranges, leaving less energy available for cognitive tasks.
Studies show that maintaining temperatures within the optimal comfort zone improves decision-making speed by 12% and reduces error rates by 8%. Consistent thermal conditions eliminate the distraction of physical discomfort, allowing employees to focus entirely on work responsibilities.
Acoustic Performance and Concentration
Sound transmission through building envelopes significantly affects workplace concentration and communication effectiveness. External noise from traffic, construction, and weather events penetrates poorly insulated walls, creating acoustic distractions that reduce productivity. Internal noise transfer between rooms and floors disrupts meetings, phone calls, and focused work activities.
Insulation materials with high Sound Transmission Class (STC) ratings absorb and block sound waves effectively. Mineral wool and spray foam systems excel at acoustic dampening while providing thermal benefits. Proper installation eliminates air gaps that compromise both thermal and acoustic performance.
Bonus Tip: Conference rooms and private offices require STC ratings of 45-50 to ensure speech privacy and minimize external distractions.
Noise Reduction Impact on Productivity
Workplace noise above 55 decibels reduces productivity by measurable amounts through increased stress hormones and decreased concentration ability. Background noise forces the brain to filter irrelevant sounds, consuming mental energy that could otherwise support work tasks. Sudden noise events cause startle responses that interrupt thought processes and require refocusing time.
Effective acoustic insulation maintains background noise levels below 45 decibels in office environments. This sound level allows normal conversation while minimizing distractions from HVAC equipment, exterior traffic, and adjacent workspace activities.
Commercial Insulation Material Performance Comparison
|
Insulation Type |
Thermal Performance (R-value/inch) |
Acoustic Rating (STC) |
Moisture Resistance |
Installation Complexity |
Durability Rating |
|
Spray Foam Closed-Cell |
R-6 to R-7 |
36-39 |
Excellent |
High |
25+ years |
|
Mineral Wool Boards |
R-4 to R-4.3 |
45-52 |
Excellent |
Moderate |
50+ years |
|
Fiberglass Batts |
R-3.1 to R-3.4 |
39-43 |
Poor |
Low |
15-25 years |
|
Rigid Foam Boards |
R-4 to R-8 |
28-35 |
Good to Excellent |
Moderate |
20-30 years |
|
Cellulose Loose-Fill |
R-3.6 to R-3.8 |
44-48 |
Fair |
Moderate |
20-30 years |
Indoor Air Quality and Health Impacts
Building envelope performance directly influences indoor air quality through moisture control and air infiltration management. Poor insulation allows uncontrolled air movement that introduces outdoor pollutants, allergens, and humidity into workspace environments. Moisture accumulation in wall cavities creates conditions for mold growth that degrades air quality and employee health.
Properly sealed insulation systems create controlled indoor environments where mechanical ventilation manages air quality effectively. Continuous insulation strategies prevent thermal bridging that causes condensation points and moisture-related issues within building assemblies.
Humidity Control and Comfort
Relative humidity levels between 40-60% optimize respiratory comfort and reduce static electricity buildup in office environments. High humidity creates stuffy conditions that cause drowsiness and discomfort. Low humidity irritates respiratory systems and increases susceptibility to airborne illnesses.
Insulation systems that include vapor barriers control moisture movement through building envelopes. This moisture management maintains stable indoor humidity levels regardless of outdoor conditions, creating healthier work environments for all occupants.
Technical Specifications for Commercial Applications
|
Performance Metric |
Open Office |
Private Office |
Conference Room |
Manufacturing |
Warehouse |
|
Minimum R-value |
R-13 to R-15 |
R-15 to R-19 |
R-19 to R-25 |
R-19 to R-30 |
R-13 to R-19 |
|
STC Rating Required |
35-40 |
40-45 |
45-50 |
25-35 |
25-30 |
|
Air Changes per Hour |
4-6 |
4-6 |
6-8 |
6-10 |
2-4 |
|
Temperature Range (F) |
70-76 |
68-76 |
68-74 |
65-78 |
60-80 |
|
Humidity Range (%) |
40-60 |
40-60 |
40-55 |
30-70 |
30-70 |
Energy Efficiency and System Performance
Well-insulated commercial buildings reduce HVAC energy consumption by 30-50% compared to poorly insulated structures. This energy efficiency translates into more stable indoor conditions because heating and cooling systems operate more consistently. Reduced equipment cycling eliminates temperature and humidity fluctuations that disrupt workplace comfort.
Continuous insulation strategies prevent thermal bridging through structural elements that create hot and cold spots within interior spaces. These temperature variations force employees to relocate or adjust personal comfort measures, reducing productivity and workspace utilization efficiency.
Bonus Tip: Buildings with thermal imaging surveys can identify insulation gaps that create localized comfort issues affecting specific workstations or departments.
Common Questions About Commercial Insulation Impact
Building age significantly influences insulation effectiveness because older structures often lack continuous insulation strategies required by modern energy codes. Retrofit insulation projects can dramatically improve workplace comfort in existing buildings, but installation methods must accommodate structural limitations and space constraints.
HVAC system sizing becomes more critical in well-insulated buildings because reduced heating and cooling loads require smaller equipment capacity. Oversized systems cycle frequently, creating temperature swings that compromise comfort. Right-sized equipment operates more efficiently and maintains steadier indoor conditions.
Zonal control systems work more effectively in properly insulated buildings because thermal zones maintain target temperatures with less energy input. This improved control allows customization of comfort conditions for different workspace types and occupancy patterns throughout the building.
Things to Consider Before Making a Decision
Building codes establish minimum insulation requirements that may not optimize workplace comfort and productivity. Energy codes focus on thermal performance while acoustic requirements often receive less attention. Workplace productivity optimization may require insulation specifications that exceed minimum code requirements.
Existing building conditions affect insulation retrofit strategies and expected performance improvements. Structural limitations, existing HVAC capacity, and renovation budgets influence material selection and installation methods. Professional energy audits identify specific comfort issues that insulation improvements can address.
Future workplace needs should guide insulation decisions because building modifications become more expensive after initial construction. Open office trends require different acoustic strategies than traditional private office layouts. Technology infrastructure and equipment heat loads influence thermal management requirements.
Productivity Research and Market Data
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory studies demonstrate that improving indoor environmental quality through better insulation increases productivity by 6-9% across various commercial sectors. The research encompasses temperature control, acoustic performance, and air quality improvements that comprehensive insulation systems provide.
The commercial insulation market reached $4.2 billion in North America during 2024, with workplace comfort optimization driving increased adoption of high-performance materials. Energy efficiency requirements and employee wellness initiatives create growing demand for insulation systems that exceed basic thermal performance standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly do employees notice comfort improvements after insulation upgrades? Most occupants detect temperature stability improvements within 24-48 hours of HVAC system adjustments following insulation installation. Acoustic improvements become apparent immediately, while air quality benefits typically develop over 2-4 weeks as indoor pollutants decrease.
Which insulation materials provide the best acoustic performance for office environments? Mineral wool and dense-pack cellulose offer superior sound absorption properties. These materials effectively reduce both airborne noise transmission and impact sounds from adjacent spaces while providing excellent thermal performance.
Can poor insulation cause sick building syndrome symptoms? Inadequate insulation contributes to temperature fluctuations, humidity problems, and air quality issues that characterize sick building syndrome. Proper insulation systems eliminate many environmental factors that cause headaches, fatigue, and respiratory irritation in commercial buildings.
Do different workspace types require specialized insulation approaches? Yes, conference rooms need higher acoustic ratings, manufacturing areas require robust thermal performance, and open offices benefit from consistent temperature distribution. Each workspace type has specific comfort requirements that influence insulation material selection and installation methods.
How does insulation affect employee absenteeism rates? Studies show that buildings with superior indoor environmental quality, including proper insulation, experience 10-15% lower absenteeism rates. Consistent comfort conditions reduce stress-related illnesses and create healthier work environments that support regular attendance.
Optimizing Your Commercial Space
Commercial insulation performance directly determines workplace comfort through temperature stability, noise control, and indoor air quality management. Effective insulation systems create environments where employees perform optimally without thermal or acoustic distractions. The building envelope's thermal integrity supports HVAC efficiency while maintaining consistent indoor conditions.
Evaluate your facility's current comfort issues and productivity challenges when selecting insulation upgrades. Consider acoustic requirements alongside thermal performance to address all environmental factors affecting employee well-being. Focus on continuous insulation strategies that eliminate thermal bridging and create uniform comfort conditions throughout your commercial space.

Reviewer: Michael Carter reviewed this article using insight gained over 12 years in the spray foam business. His feedback focused on helping contractors reach new customers without overcomplicating their message...