Unlocking the Future of Filmmaking: What is Virtual Production?
Virtual production is transforming the filmmaking landscape, merging cutting-edge technology with creative storytelling to redefine how films, TV shows, and other visual media are created. By blending real-time rendering, advanced visual effects, and innovative production techniques, virtual production enables filmmakers to craft immersive worlds with unprecedented flexibility and efficiency.

Virtual production is transforming the filmmaking landscape, merging cutting-edge technology with creative storytelling to redefine how films, TV shows, and other visual media are created. By blending real-time rendering, advanced visual effects, and innovative production techniques, virtual production enables filmmakers to craft immersive worlds with unprecedented flexibility and efficiency. In this guest post, well dive into the essence of virtual production, explore its key components, benefits, and real-world applications, and discuss why its becoming a cornerstone of modern filmmaking.
What is Virtual Production?
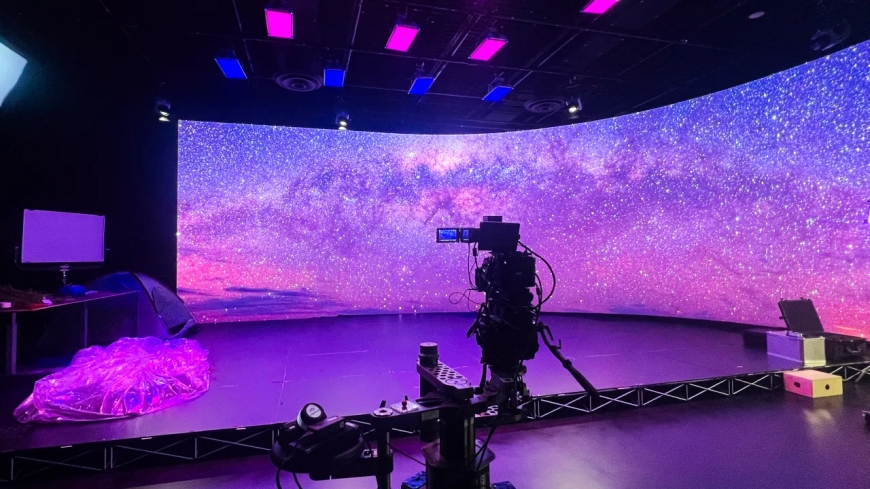
At its core, virtual production is a filmmaking process that integrates physical and digital elements in real time to create dynamic, interactive environments for storytelling. Unlike traditional filmmaking, which often relies on post-production to add visual effects or green screens to simulate environments, virtual production allows directors, actors, and crew to visualize and interact with digital sets, characters, and effects during principal photography. This is achieved through technologies like real-time game engines, LED walls, motion capture, and augmented reality.
The term "virtual production" gained prominence with projects like Disneys The Mandalorian, which used a massive LED wall to display photorealistic backgrounds, allowing actors to perform within fully realized digital environments. However, virtual production is not limited to high-budget Hollywood productionsits increasingly accessible to independent filmmakers, game developers, and content creators across various industries.
Key Components of Virtual Production
Virtual production is a multifaceted process that relies on several interconnected technologies and techniques. Here are the primary components that make it possible:
-
Real-Time Rendering Engines
Game engines like Unreal Engine and Unity are the backbone of virtual production. These engines render high-quality visuals in real time, allowing filmmakers to see the final look of a scene as its being shot. This eliminates the guesswork associated with green-screen shoots, where the environment is added in post-production. -
LED Walls and Virtual Sets
Large-scale LED walls, often referred to as "volume stages," display dynamic, photorealistic backgrounds that react to camera movements. These walls create immersive environments that actors can see and interact with, enhancing performances and reducing the need for extensive post-production work. -
Motion Capture and Performance Capture
Motion capture technology tracks actors movements and facial expressions, translating them into digital characters in real time. This is particularly useful for creating CGI characters or creatures that need to integrate seamlessly with live-action footage. -
Camera Tracking and Virtual Cinematography
Advanced camera tracking systems synchronize physical camera movements with the virtual environment. This ensures that the perspective and lighting of the digital background align perfectly with the physical camera, creating a cohesive visual experience. -
Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR)
AR and MR tools allow filmmakers to overlay digital elements onto the physical world, enabling directors to preview scenes, adjust lighting, or place virtual objects during production. -
Previsualization (Previs)
Virtual production often begins with previs, a process where filmmakers create rough digital versions of scenes to plan shots, test ideas, and refine creative decisions before shooting begins. This saves time and resources during production.
The Benefits of Virtual Production
Virtual production offers a range of advantages that are revolutionizing the filmmaking process. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Enhanced Creative Control
With virtual production, directors and cinematographers can see the final environment in real time, allowing them to make creative decisions on the spot. This eliminates the disconnect between whats shot on set and whats finalized in post-production, resulting in a more cohesive vision.
2. Cost and Time Efficiency
While the initial investment in virtual production technology can be significant, it often reduces costs in the long run. By minimizing the need for location shooting, physical set construction, and extensive post-production, virtual production streamlines workflows and accelerates production timelines.
3. Realistic Lighting and Reflections
LED walls provide dynamic lighting that interacts naturally with actors and physical props, creating realistic reflections and shadows. This eliminates the artificial look often associated with green-screen compositing, enhancing the visual quality of the final product.
4. Flexibility and Iteration
Virtual production allows filmmakers to make real-time adjustments to digital environments, such as changing lighting, weather, or set designs without halting production. This flexibility encourages experimentation and innovation.
5. Accessibility for Smaller Productions
As virtual production tools become more affordable, independent filmmakers and smaller studios can adopt these techniques. Cloud-based rendering, affordable motion capture systems, and open-source game engines are democratizing access to high-quality production methods.
6. Sustainability
By reducing the need for physical sets and location shoots, virtual production minimizes the environmental impact of filmmaking. Fewer travel logistics and physical materials contribute to a greener production process.
Real-World Applications of Virtual Production
Virtual production is not limited to blockbuster films. Its versatility has led to widespread adoption across various industries and formats. Here are some notable applications:
1. Film and Television
High-profile projects like The Mandalorian, The Batman, and Avatar: The Way of Water have showcased the power of virtual production. LED walls and real-time rendering have enabled filmmakers to create expansive worlds, from alien planets to futuristic cities, without leaving the studio.
2. Commercials and Advertising
Virtual production is ideal for creating visually striking commercials in controlled environments. Brands can craft tailored, immersive worlds to showcase products, all while keeping production costs and timelines manageable.
3. Music Videos
Artists and directors use virtual production to create surreal, visually captivating music videos. The ability to manipulate environments in real time allows for bold, creative visuals that align with the musics tone and message.
4. Gaming and Interactive Media
Game developers use virtual production techniques to create cinematic cutscenes and immersive worlds. The same real-time rendering engines used in filmmaking are often employed in game development, blurring the lines between the two industries.
5. Live Events and Broadcasts
Virtual production is increasingly used in live broadcasts, such as sports events, news programs, and virtual concerts. AR overlays and virtual sets enhance viewer experiences by adding dynamic graphics and interactive elements.
6. Education and Training
Virtual production is also making waves in education, where its used to create immersive training simulations for fields like medicine, aviation, and military operations. These simulations provide realistic, interactive environments for hands-on learning.
Challenges and Considerations
While virtual production offers immense potential, its not without challenges. The technology requires significant upfront investment in equipment, software, and skilled personnel. Training crew members to operate complex systems like LED walls and game engines can be time-consuming. Additionally, the reliance on technology means that technical glitches or compatibility issues can disrupt production if not managed properly.
Another consideration is the learning curve for traditional filmmakers transitioning to virtual production. Directors and cinematographers accustomed to conventional methods may need time to adapt to real-time workflows and digital tools. However, as the technology becomes more user-friendly and widespread, these barriers are gradually diminishing.
The Future of Virtual Production
The future of virtual production is bright, with rapid advancements in technology paving the way for even more innovative applications. Here are some trends to watch:
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence is being integrated into virtual production workflows, from generating realistic digital environments to automating camera tracking and lighting adjustments.
- Cloud-Based Collaboration: Cloud rendering and remote collaboration tools are making virtual production more accessible, allowing global teams to work together seamlessly.
- Immersive Storytelling: As virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies evolve, virtual production will play a key role in creating interactive, immersive narratives for audiences.
- Miniaturization of Technology: Smaller, more affordable LED walls and motion capture systems are making virtual production viable for independent creators and smaller studios.
Getting Started with Virtual Production
For filmmakers and content creators interested in exploring virtual production, here are some practical steps to get started:
- Learn the Tools: Familiarize yourself with real-time rendering engines like Unreal Engine or Unity. Many online tutorials and courses are available for beginners.
- Invest in Equipment: Depending on your budget, consider investing in LED screens, motion capture systems, or high-performance computers for rendering.
- Collaborate with Experts: Partner with VFX artists, game developers, or virtual production specialists to bridge the gap between traditional filmmaking and digital workflows.
- Experiment with Previs: Start with previsualization to test ideas and workflows before committing to a full virtual production setup.
- Stay Updated: Follow industry trends and advancements in virtual production technology to remain competitive.
Conclusion
Virtual production is more than a technological trendits a paradigm shift thats redefining the art and craft of filmmaking. By combining real-time rendering, LED walls, motion capture, and other cutting-edge tools, virtual production empowers creators to push creative boundaries, reduce costs, and tell stories in ways that were once unimaginable. Whether youre a seasoned filmmaker or an aspiring content creator, embracing virtual production opens up a world of possibilities to bring your vision to life.
As the technology continues to evolve, virtual production will undoubtedly become a standard tool in the filmmakers toolkit, bridging the gap between imagination and reality. So, what are you waiting for? Dive into the world of virtual production and unlock the future of storytelling.